Stereotaxic Body Radiosurgery
The principles of SRS, that is, high-precision radiation, are currently being used to treat tumors in the body, in a procedure called Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy (SBRT).
High doses in few treatments (1-5 treatments) SBRT is currently used in the treatment of small to medium-sized malignant or benign tumors in the body and in common disease sites, such as metastases in: Lung, liver, abdomen , spine, prostate, breasts and head and neck mainly.
Despite its name and compared to traditional radiation therapy, it is a non-surgical procedure that delivers highly focused radiation at much higher doses and in only one or a few treatments. This treatment is possible thanks to the development of highly advanced radiation technologies that allow the delivery of maximum doses within the target, while maximizing the dose received by the surrounding healthy tissue. The goal is to administer doses that destroy the tumor and achieve maximum local control.
Special preparations needed for the procedure
SBRT is administered with the help of a team of radiation therapy personnel, which typically includes a radiation oncologist, a radiation therapy nurse, and an imaging specialist, plus a physicist and a dosimetrist. Before your treatment begins, you will have one or more appointments with your team members to make the necessary plans and preparations for your treatment; This may require you to undergo other tests and procedures. Before your first treatment session:
- Maybe you have to implement some markers fiducials (also called seeds) in or near the tumor. Markers are small segments of metallic gold that are clearly seen on imaging studies and later guide radiation therapy treatment. Your doctor will explain this procedure to you in more detail, if necessary.
- You may have CT scans or other imaging tests to pinpoint the places in your body that will be treated with radiation therapy.
- Positioning devices such as molds, masks, supports and cushions are made to help keep your body in the same position during each treatment session.

SRBT treatment sessions
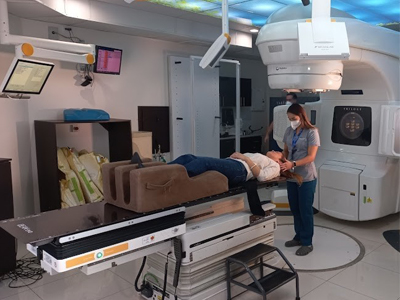
In SBRT, 1 to 5 doses of radiation are given over 1 to 2 weeks. You and your team members will discuss the exact schedule of your treatment beforehand. Each treatment session lasts 60-90 minutes. During each session, you can expect the following to occur:
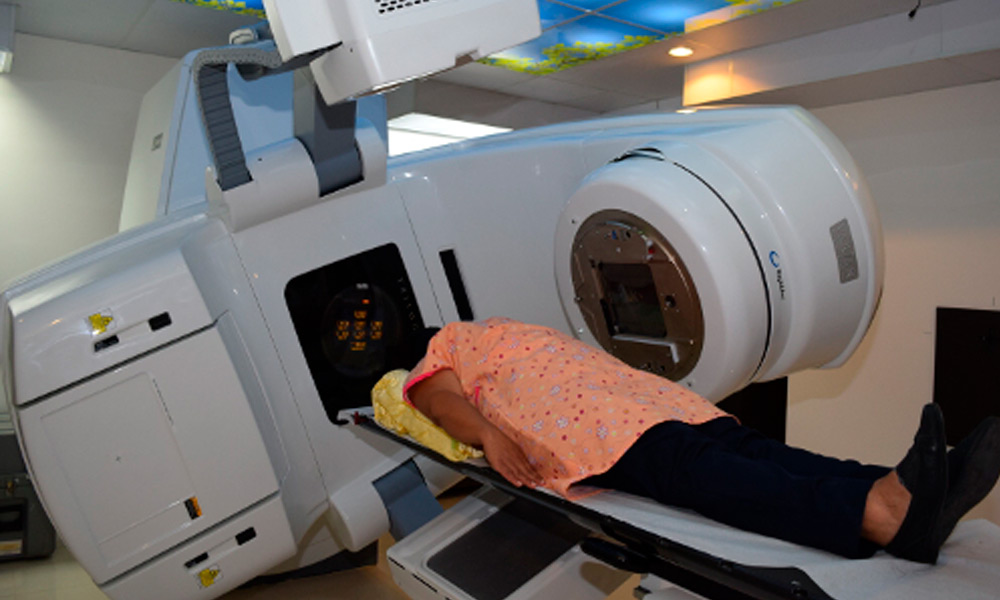
- You take off your clothes and put on a patient gown. The imaging doctor places it in the correct position on a treatment table; At this time, whatever positioning device has been developed is used.
- The imaging doctor leaves the room and turns on the linac from outside. The imaging doctor will watch you on a monitor and you will be able to talk to him through an intercom.
- With the help of x-rays or tomography, the correct positioning and alignment of the linac beams with respect to your body is confirmed; The beams are then directed towards the tumor. You will hear the device but you will not feel anything.
- You will be able to return home shortly after your treatment session ends. Your doctor or nursing staff will tell you when to return for your next session, if you need to return.
Possible side effects of SRBT
With any type of radiation therapy, healthy cells and tissue surrounding the tumor may also be affected by the treatment. This can cause side effects such as fatigue and skin changes. Most side effects disappear shortly after treatment ends; However, some do not appear until months or even years after treatment. The type and severity of side effects you have will depend on the amount of radiation given and where in the body you are treated. Your doctor can give you more information about the side effects you can expect and what you can do to control them. If necessary, medications may be prescribed to treat some side effects. Members of your healthcare team can also teach you methods to deal with side effects.