Colorectal Cancer and its Treatment
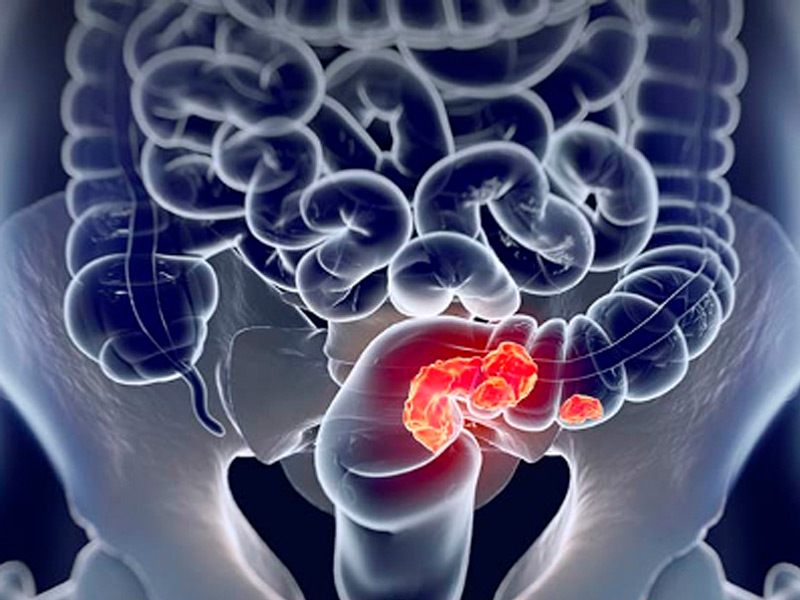
What is colorectal cancer?
He rectal cancer It is defined as the tumor located between the anal margin and 15 cm proximally. In rectal cancer, accurate preoperative staging allows patients to be correctly classified for the various existing therapies, as well as to select the best surgical treatment.
RISK FACTOR'S
Aging is the most important risk factor for most cancers. Other risk factors for colorectal cancer include:

FAMILY BACKGROUND: Colorectal cancer in a first-degree relative.
PERSONAL HISTORY: From colorectal adenomas, colorectal cancer or ovarian cancer.
Hereditary Conditions: Such as familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP) and Lynch syndrome (hereditary nonpolyposis colon cancer [HNPCC])
EXCESSIVE ALCOHOL CONSUMPTION
TOBACCO
AFRICAN AMERICAN RACE OR ETHNICITY
OBESITY
Clinic Features
The symptoms of rectal cancer are similar to those of colon cancer and will depend on the time of evolution and its location (distance from the anal margin, location on the anterior wall, circumferential, etc.), including the following:
SYMPTOMS: Rectal bleeding, Change in bowel habit, Abdominal pain, Intestinal obstruction, Change in appetite, Weight loss, Weakness.
With the exception of symptoms of obstruction, these symptoms do not always correlate with the stage of the disease or signify a particular diagnosis.
DIAGNOSIS: The way to make the diagnosis is within the reach of every doctor and only consists of a digital rectal examination (DRE) in which an irregular tumor mass that is generally hard and usually fixed will be palpated. It is also believed that currently not only the digital rectal examination should be considered in the diagnosis but also the low endoscopic study (colonoscopy) in all patients over 40 years of age who consult for hematochezia (elimination of visible blood from the rectum). The finding of neoplastic lesions in the endoscopic examination will be accompanied by the anatomopathological study of biopsies which should confirm the diagnosis of adenocarcinoma.
STAGING
In patients with CR, staging is essential not only to estimate the prognosis but also to define the different therapeutic alternatives. Let us remember that the surgeon must decide whether the patient should undergo preoperative chemoradiotherapy, decide the surgical technique (anterior resection with or without preservation of the sphincter apparatus, local trans-anal resection) and discuss in detail any possible sequelae. For all these decisions, it is essential to carry out an optimal study and preoperative staging. This staging will undergo changes in patients undergoing preoperative chemoradiotherapy since as a result of its effectiveness a marked reduction in tumor mass (wall and lymph node) will be obtained in more than 70% of patients and even a complete tumor response in around a 10 to 20% of them.
Below are the details of some of these treatments:
SURGICAL TREATMENT: Surgery is the fundamental basis for the successful treatment of colorectal carcinoma. Its objective is the removal of the primary tumor and any loco-regional extension that may have occurred, without causing tumor spread and with the best quality of life for the patient.
CHEMOTHERAPY TREATMENT: When choosing the chemotherapy regimen to be administered, the activity and tolerance of the chemotherapy regimen and a series of factors that depend on the patient (will, general condition, comorbidity, etc.) are taken into account. It increases survival and can be given palliatively in very advanced cancers.
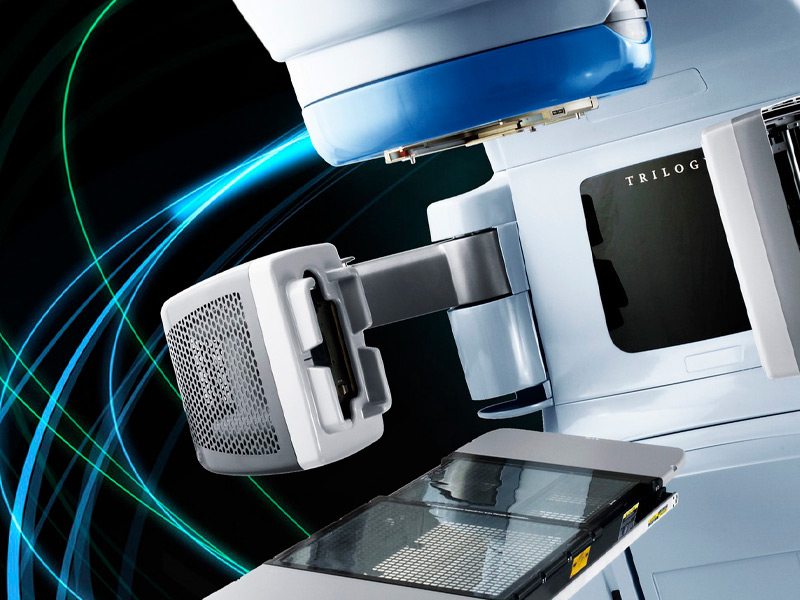
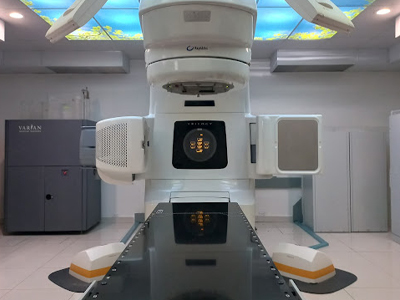
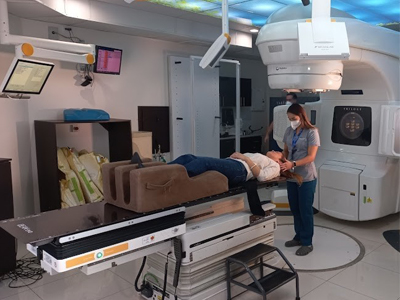
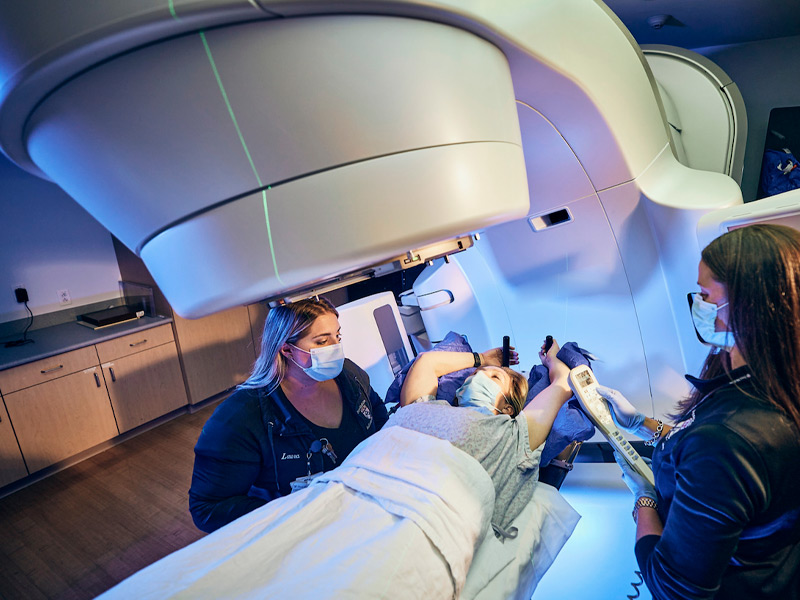
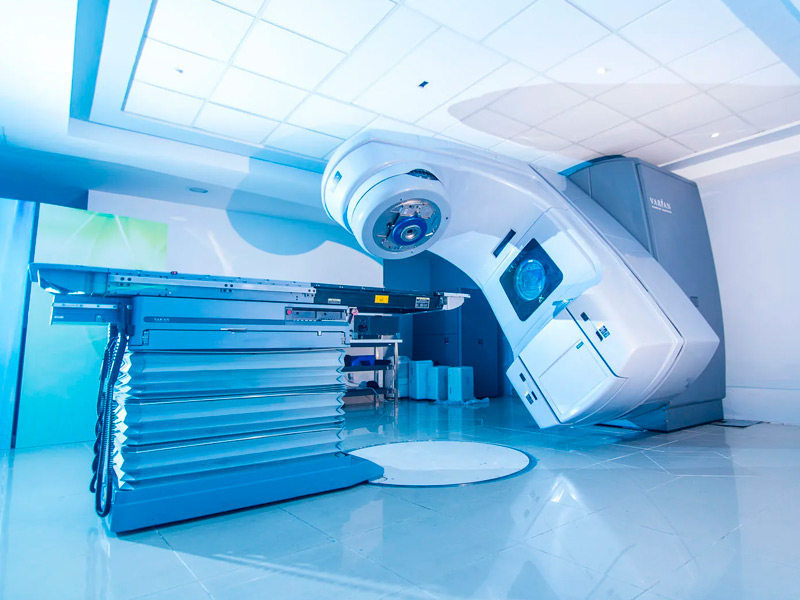
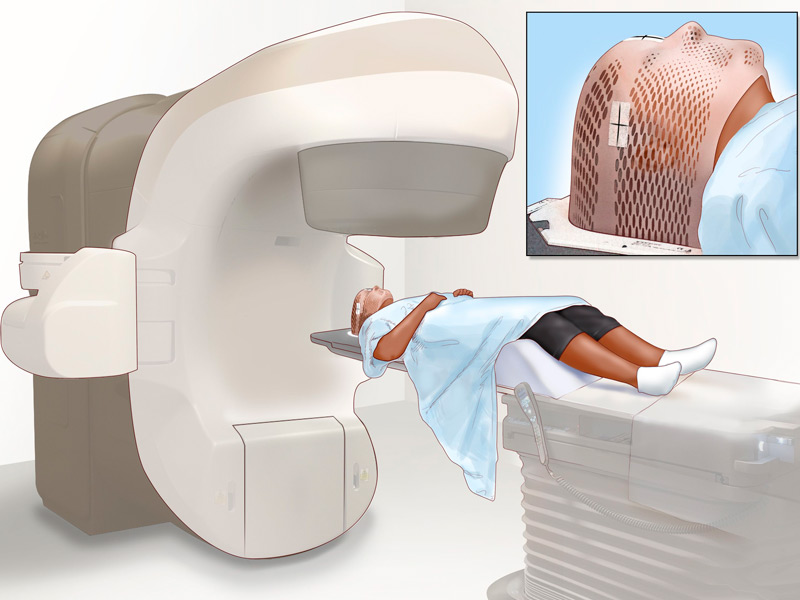
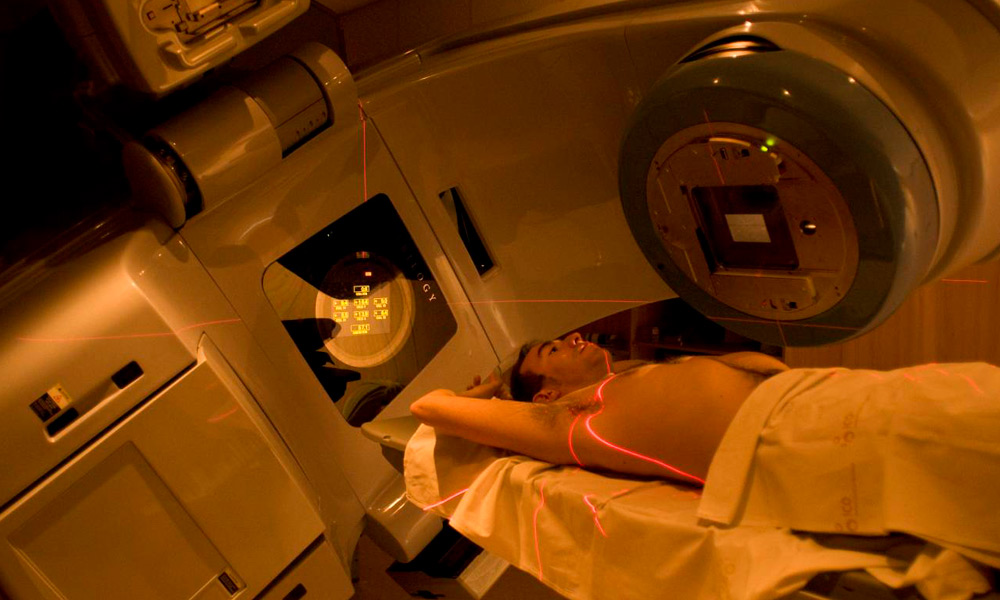
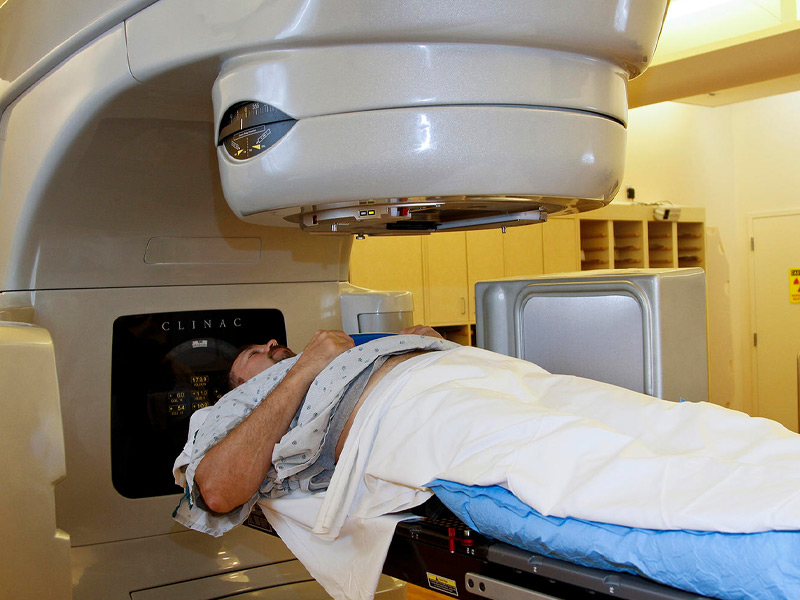
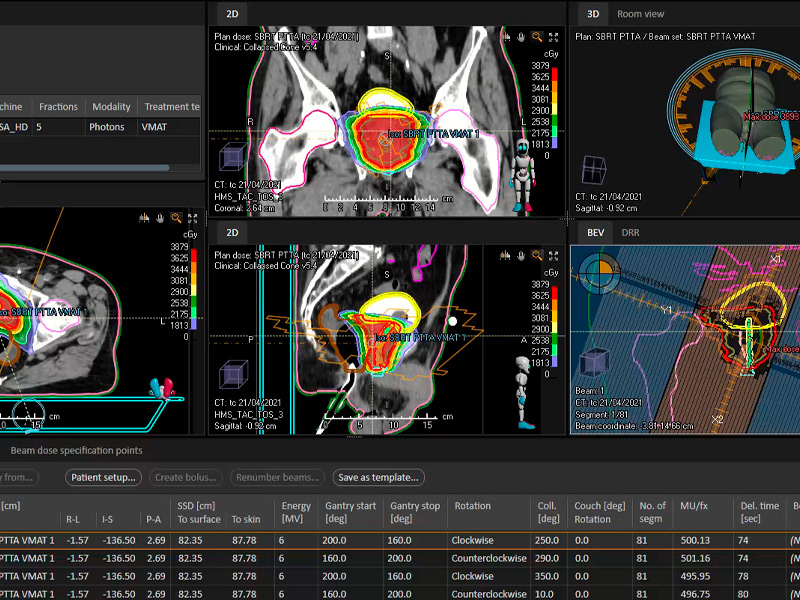
RADIOTHERAPY TREATMENT: The use of radiotherapy as part of the treatment of rectal malignancies is increasingly widespread. In locally advanced primary rectal cancer, several studies have demonstrated its effectiveness, with a decrease in local recurrence and an increase in disease-free survival, both in its preoperative and postoperative administration. Emerging developments such as intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT), image-guided radiation therapy (IGRT), and stereotactic radiation therapy (SBRT) are being evaluated. These techniques offer the possibility of providing greater radiotherapy without involving normal or healthy tissue.
Currently the 21st Century Radiotherapy Clinic has the technology and experience to treat this type of diseases, guaranteeing the protection of surrounding organs and tissues, thus providing a higher quality of life for the patient.
When is radiation therapy used to treat colorectal cancer?
Before and/or after surgery to help prevent the cancer from coming back. In this case, it is often given together with chemotherapy. Many doctors now favor giving radiation therapy before surgery because it can make it easier to remove the cancerous tumor.
With or without chemotherapy to help control rectal cancers in people who are not healthy enough to have surgery or to relieve symptoms in people with advanced cancer that is causing intestinal blockage, bleeding, or pain.
To re-treat tumors that have returned in the pelvic region after undergoing radiotherapy.
To help treat cancer that has spread to other areas (Metastases), such as bones, liver, brain.